Attention: this post is so big that it broke Discourse’s 32k character limit, so I had to split it into two parts. Part 2 will be posted in the replies. Please don’t reply until you see part 2 posted below.
Hello everyone, it’s ya boy with another extension. Last time I said I’d return with a bigger extension, so here I am, after 3 weeks of pouring digital blood, sweat and tears into this extension. This is by far the biggest extension I’ve ever created - adding 60 blocks with ~1300 lines of extension code and nearly as many lines of testing code.
So, you can expect this not only to be my biggest, but also most polished extension, as it’s been thoroughly (questionable) tested.
Before going any further, it’s important to clarify a few things. Firstly, this extension does not add a new category to the block toolbar. It just adds new blocks to the default Arrays category. In JavaScript, you can find the methods in the arrays namespace.
So, without further ado, let’s jump into it.
Blocks
As you can see below, this extension adds two new groups to the Arrays category, “Checks” and “Mutual Operations” (they weren’t there before).
Create
The Create category contains blocks that create entirely new arrays from given values. BetterArrays adds 2 new blocks to it.
Repeat
The repeat method creates an array by repeating an element a given number of times. This behaviour is inspired by Python’s [item]*repeat syntax.
function repeat(item: any, repeat: number): any[]
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns ["foo", "foo", "foo"]
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE is thrown if repeat is not an integer
NEGATIVE_VALUE is thrown if repeat is a negative number
Range
The range method creates a range of numbers starting from start, ending with end (not included) while increasing each value in the range by step (optional; default is 1)
function range(start: number, end: number, step: number): number[]
![]()
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example will return [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
![]()
This example will return [0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE is thrown if start, end, or step are not integers
NEGATIVE_VALUE is thrown if step is a negative number
ZERO_STEP is thrown if step is equal to 0
INVALID_RANGE is thrown if end is lower than start
Read
The Read category contains blocks that read data from arrays. BetterArrays adds 9 new blocks to it.
Find Last
The findLast method returns the index of the last occurrence of an item in an array.
Returns -1 if the item is not found.
function findLast(array: any[], item: any): number
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns 2 (because the last occurrence of “foo” is at index 2)
![]()
This example returns -1 because “baz” is not in the array.
Find All
The findAll method returns an array of indicies pointing to every occurrence of an item. You can use max to limit the number of indicies that are retrieved (default is 0, which is unlimited).
function findAll(array: any[], item: any, max: number): number[]
![]()
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns [0, 2] (because “foo” appears on indicies 0 and 2)
![]()
This example returns [0] (because number of found indicies is limited to 1)
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE is thrown if max is not an integer
NEGATIVE_VALUE if max is a negative number
Count
The count method counts the number of times an item occurs in an array.
function count(array: any[], item: any): number
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns 2 (because “foo” occurs twice in the array)
Convert to string
The toString method converts an array to a string.
function toString(array: any[]): string
![]()
Random Index
The randomIndex method returns a random index from an array.
function randomIndex(array: any[]): number
![]()
Exception
EMPTY_ARRAY is thrown if array is empty
Min Index
The minIndex method returns the index of the smallest element from a number array.
function minIndex(array: number[]): number
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns 2 (2 is the index of the biggest element, 2)
Exceptions
EMPTY_ARRAY is thrown if array is empty
Min
The min method returns the smallest element from a number array.
function min(array: number[]): number
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns 2
Exceptions
EMPTY_ARRAY is thrown if array is empty
Modify
The Modify category contains blocks that modify arrays directly. BetterArrays adds 18 new blocks to it.
Remove All
The removeAll method removes all occurrences of item from an array. You can use max (default is 0, which is unlimited) to limit the number of items removed. This method modifies the original array.
function removeAll(array: any[], item: any, max: number): void


Examples
In this example list becomes ["bar"] (both “foo” elements are removed)
In this example list becomes ["bar", "foo"] (the first and second “foo” are removed, leaving “bar” and the last “foo”)
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE is thrown if max is not an integer
NEGATIVE_VALUE is thrown if max is negative
Swap
The swap method swaps items at first and second indicies in an array. This method modifies the original array.
function swap(array: any[], first: number, second: number): void

Examples
In this example, list becomes ["baz", "bar", "foo"] (because the first and last items are swapped)
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE is thrown if first or second are not integers
NEGATIVE_VALUE is thrown if first or second are negative
OUT_OF_RANGE is thrown if first or second are out of array range
Replace
The replace method replaces all elements in an array matching item with replacement. This method modifies the original array.
function replace(array: any[], item: any, replacement: any): void

Examples
In this example list becomes ["bar", "bar", "baz"] (“foo” is replaced with “bar”)
Fill
The fill method fills an item with a static item from a start (optional; default is 0) index to an end (optional; default is array lenght; end index is excluded) index. This method modifies the original array.
function fill(array: any[], item: any, start: number, end: number): void



Examples
In this example list becomes ["bam", "bam", "bam"] (array is completely filled)
In this example list becomes ["foo", "bam", "bam"] (filled from 1 to end)
In this example list becomes ["bam", "bam", "baz"] (filled from 0 to 2, not including 2, so only items at indicies 0 and 1 are set)
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE is thrown if start or end are not integers
NEGATIVE_VALUE is thrown if start or end are negative
OUT_OF_RANGE is thrown if start or end are out of array range
INVALID_RANGE is thrown if end is smaller than start
Concatenate
The concat method concatenates (adds) a second array to the end of an array. This mehtod modifies the first array.
function concat(first: any[], second: any[]): void

Examples
In this example list becomes ["foo", "bar", "baz", "bam"] (["foo", "bar"] + ["baz", bam"] = ["foo", "bar", "baz", "bam"])
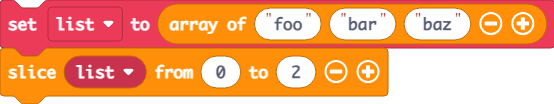
Slice
The slice extension slices an array from a start (optional; default is 0) index to an end (optional; default is array length; end index is excluded) index, with an optional step value. This method modifies the original array.
function slice(array: any[], start: number, end: number, step: number): void




Examples
In this example list does not change its value (because the array is sliced from start to end. I’m not sure why this feature exists)
In this example list becomes ["bar", "baz"] (the list is sliced from index 1, leaving index 0 out)
In this example list becomes ["foo", "bar"] (the list is sliced from 0 to 2, where 2 is excluded, so “baz” is excluded)
In this example list becomes ["foo", "baz"] (starting at index 0, the method steps two elements forward to index 2, which gets “baz” and skips “bar”)
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE is thrown if start, end or step are not integers
NEGATIVE_VALUE is thrown if start, end or step are negative
OUT_OF_RANGE is thrown if start or end are out of list range
ZERO_STEP is thrown if step is 0
INVALID_RANGE is thrown if end is smaller than start
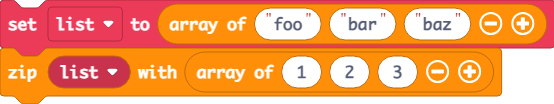
Zip
The zip method creates an array of pairs by grouping elements from two arrays. If the arrays are not the same length, excess items in the longer array will be ignored. This method modifies the first array.
function zip(first: any[], second: any[]): void

Examples
In this example list becomes [["foo", 1], ["bar", 2], ["baz", 3]]
In this example list becomes [["foo", 0], ["bar", 1]] (3rd item is ignored because shorter array length is 2)
Clear
The clear method clears the array. This method modifies the original array.
function clear(array: any[]): void

Examples
In this example list becomes []
Union
The union method creates a union (all elements from both arrays together, no duplicates) from two arrays. This method modifies the first array.
function union(first: any[], second: any[]): void

Examples
In this example list becomes ["foo", "bar", "baz"] (elements from both arrays, but with “bar” appearing once because it’s a duplicate)
Intersection
The intersection method creates an intersection (only elements that appear in both arrays, no duplicates) from two arrays. This method modifies the first array.
function intersection(first: any[], second: any[]): void

Examples
In this example list becomes ["bar"] (only “bar” is in both arrays)
Difference
The difference method creates a difference (elements that appear in the first array, without the items from the second array) from two arrays. This method modifies the first array.
function difference(first: any[], second: any[]): void

Examples
In this example list becomes ["foo"] (“bar” is removed because it’s also in the second array)
Purge (Remove Duplicates)
The purge method removes duplicate elements from an array. This method modifies the original array.
function purge(array: any[]): void

Examples
In this example list becomes ["foo", "bar"] (the duplicate “foo” is removed)
Sort
The sort method sorts a number array in ascending or descending order. String arrays may be supported in the future. This method modifies the original array.
function sort(array: number[], order: SortOrder): void


Examples
In this example list becomes [1, 2, 3]
In this example list becomes [3, 2, 1]
Enumerate
The enumerate method enumerates elements of an array (creates value-index pairs). This method modifies the original array.
function enumerate(array: any[]): void

Examples
In this example list becomes [["foo", 0], ["bar", 1], ["baz", 2] (value-index pairs from array)
Splice
The splice method deletes count elements from start index in an array. This method modifies the original array.
function splice(array: any[], start: number, count: number): void

Examples
In this example list becomes [1] (2 elements starting from 0 were removed)
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE is thrown if start or count are not integers
NEGATIVE_VALUE if start or count are negative
Unzip
The unzip method extracts elements from an array of pairs, at target index. This method modifies the original array.
function unzip(array: any[][], target: number): void

Examples
In this example list will become ["a", "b"] (Gets index 0 from every pair)
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE is thrown if target is not an integer
NEGATIVE_VALUE if target is negative
NOT_ARRAY if element to unpack is not an array (every element must be an array)
OUT_OF_RANGE if target index is bigger than pair length
Shift
The shift method shifts all elements in the array backwards by elements. This method modifies the original array.
function shift(array: any[], elements: number): void

Examples
In this example list becomes [2, 3]
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE is thrown if elements is not an integer
NEGATIVE_VALUE is thrown if elements is negative
INVALID_SHIFT is thrown if elements is bigger than array length
Flatten
The flatten method unpacks arrays within an array recursively to the surface level up to a max depth value (default is 0, which is unlimited). This method modifies the original array.
function flatten(array: any[], max: number): void


Examples
In this example, list becomes [1, 2, 3, 4]
In this example list becomes [1, 2, [3, 4]] (because it only unpacks the first layer)
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE is thrown if max is not an integer
NEGATIVE_VALUE is thrown if max is negative
Operations
The Operation category contains blocks that perform various operations on arrays, without modifying the original array. BetterArrays adds 21 new blocks to it.
To Shifted
The toShifted method (equivalent to shift) returns a copy of the array with all elements in the array shifted backwards by elements. This mehod does not modify the original array.
function toShifted(array: any[], elements: number): void
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns ["bar", "baz"]
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE is thrown if elements is not an integer
NEGATIVE_VALUE is thrown if elements is negative
INVALID_SHIFT is thrown if elements is bigger than array length
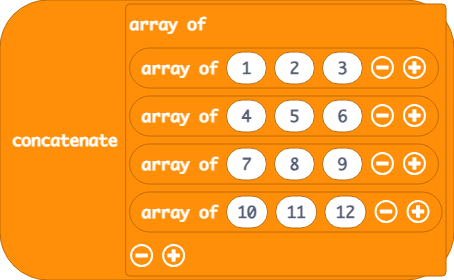
Concatenate Many
The concatMany returns a concatenation (addition) of an array of arrays. This method does not modify the original array.
function concatMany(arrays: any[][]): any[]
![]()
Examples
This example returns [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12]
Zip Many
The zipMany method returns an array of pairs by grouping elements from multiple arrays. If the arrays are not the same length, excess items in the longer array(s) will be ignored.
function zipMany(arrays: any[]): any[][]
![]()
Examples
This example returns [[1, 4, 7, 10], [2, 5, 8, 11], [3, 6, 9, 12]]
![]()
This examples [["a", 0], ["b", 1]] (3rd element is ignored because shortest array has length 2)
To Flattened
The toFlattened method (equivalent to flatten) returns a copy of an array with arrays within unpacked recursively to the surface level up to a max depth value (default is 0, which is unlimited). This method does not modify the original array.
function toFlattened(array: any[], max: number): any[]
![]()
![]()
Examples

This example returns [1, 2, 3, 4]
![]()
This example returns [1, 2, [3, 4]]
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE is thrown if max is not an integer
NEGATIVE_VALUE is thrown if max is negative
Copy
The copy method returns a copy of the array (new array with same items). This method does not modify the original array.
function copy(array: any[]): void
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns ["foo", "bar"] (who could have predicted that?)
To Removed All
The toRemovedAll method returns an array copy with all occurrences of item removed. You can use max (default is 0, which is unlimited) to limit the number of items removed. This method does not modify the original array.
function toRemovedAll(array: any[], item: any, max: number): any[]
![]()
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns ["bar"]
![]()
This example returns ["bar", "foo"] (second “foo” is not removed because max is 1)
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE is thrown if max is not an integer
NEGATIVE_VALUE is thrown if max is negative
To Swapped
The toSwapped method returns an array copy with swapped items at first and second indicies. This method does not modify the original array.
function toSwapped(array: any[], first: number, second: number): any[]
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns ["baz", "bar", "foo"]
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE is thrown if first or second are not integers
NEGATIVE_VALUE is thrown if first or second are negative
OUT_OF_RANGE is thrown if first or second are out of array range
To Replaced
The toReplaced method returns an array copy with all elements matching item replaced with replacement. This method does not modify the original array.
function toReplaced(array: any[], item: any, replacement: any): any[]
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns ["baz", "bar", "baz"]
To Filled
The toFilled method returns an array copy filled with a static item from a start (optional; default is 0) index to an end (optional; default is array lenght; end index is excluded) index. This method does not modify the original array.
function toFilled(array: any[], item: any, start: number, end: number): any[]
![]()
![]()
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns ["bam", "bam", "bam"]
![]()
This example returns ["foo", "bam", "bam"]
![]()
This example returns ["bam", "bam", "baz"]
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE is thrown if start or end are not integers
NEGATIVE_VALUE is thrown if start or end are negative
OUT_OF_RANGE is thrown if start or end are out of array range
INVALID_RANGE is thrown if end is smaller than start
To Sliced
The toSliced method returns a slice of an array from a start (optional; default is 0) index to an end (optional; default is array length; end index is excluded) index, with an optional step value. This method does not modify the original array.
function toSliced(array: any[], start: number, end: number, step: number): any[]
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns ["foo", "bar", "baz"] (for some reason)
![]()
This example returns ["bar", "baz"]
![]()
This example returns ["foo", "bar"] (index 2 is excluded)
![]()
This example returns ["foo", "baz"]
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE is thrown if start, end or step are not integers
NEGATIVE_VALUE is thrown if start, end or step are negative
OUT_OF_RANGE is thrown if start or end are out of list range
ZERO_STEP is thrown if step is 0
INVALID_RANGE is thrown if end is smaller than start
To Zipped
The toZipped method returns an array of pairs created from two arrays. If the arrays are not the same length, excess items in the longer array will be ignored.
function toZipped(first: any[], second: any[]): any[][]
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns [["foo", 1], ["bar", 2], ["baz", 3]]
![]()
This example returns [["foo", 1], ["bar", 2]] (3rd element from first array is ignored because second array length is 2)
To Reversed
The toReversed method returns a reversed copy of an array.
function toReversed(array: any[]): any[]
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns ["baz", "bar", "foo"]
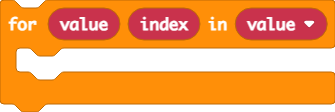
For Each
The forEach method loops through an array with value and index parameters. You can drag any blocks into the handler to execute them within the loop using the parameters.
function forEach(array: any[], handler: (value: any, index: number) => void): void
Examples
This example logs
0 = foo
1 = bar
2 = baz
to the console
To Purged
The toPurged method returns an array copy with all duplicates removed.
function toPurged(array: any[]): any[]
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns ["foo", "bar"]
Extract
The extract method returns an array comprised of every occurrence of an item in an array.
function extract(array: any[]): any[]
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns ["foo", "foo"] (the first and last element are extracted from the original array and returned in a new array)
To Sorted
The toSorted method returns a sorted number array copy in ascending or descending order. String arrays may be supported in the future. This method does not modify the original array.
function toSorted(array: number[], order: SortOrder): number[]
![]()
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns [1, 2, 3]
![]()
This example returns [3, 2, 1]
Sum
The sum method returns a sum of elements in a number array.
function sum(array: number[]): number
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns 6
To Enumerated
The toEnumerated method returns enumerated elements of an array (creates value-index pairs). This method does not modify the original array.
function toEnumerated(array: any[]): any[]
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns [["foo", 0], ["bar", 1], ["baz", 2]]
Join
The join method returns a string array joined into a single string using a separator (optional; default is nothing).
function join(array: string[]): string
![]()
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns foobarbaz
![]()
This example returns foo-bar-baz
To Spliced
The toSpliced method returns an array copy with count elements deleted from start index. This method does not modify the original array.
function toSpliced(array: any[], start: number, count: number): any[]
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns ["baz"]
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE is thrown if start or count are not integers
NEGATIVE_VALUE is thrown if start or count are negative
OUT_OF_RANGE is thrown if start is out of array range
To Unzipped
The toUnzipped method returns extracted elements from an array of pairs, at target index. This method does not modify the original array.
function toUnzipped(array: any[], target: number): any[]
![]()
Examples
![]()
This example returns ["foo", "bar"] (extracts every element at index 0)
Exceptions
NON_INTEGER_VALUE if target is not an integer
NEGATIVE_VALUE if target is negative
NOT_ARRAY if element to unpack is not an array (every element must be an array)
OUT_OF_RANGE if target is bigger than pair length